How AI Agents Work: The Complete Guide to Understanding AI Agent Architecture
Artificial intelligence has evolved far beyond simple chatbots and automated responses. Modern AI agents represent a revolutionary leap forward, capable of autonomous decision-making, complex problem-solving, and continuous learning. Understanding how AI agents work is crucial for businesses looking to leverage these intelligent systems for competitive advantage.
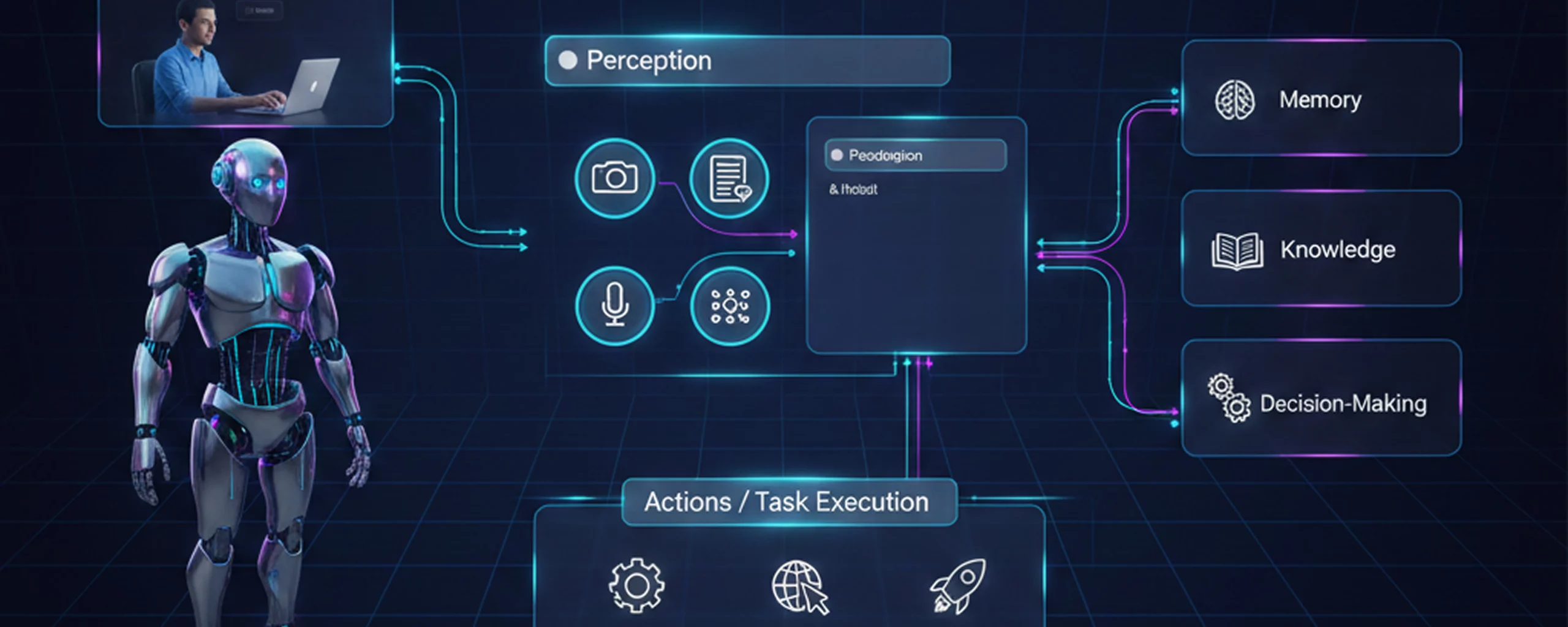
AI agents operate through sophisticated architectures that combine perception, reasoning, and action in continuous cycles. Unlike traditional AI systems that simply respond to inputs, these agents actively plan, execute tasks, and adapt their behavior based on experience and environmental feedback.
This comprehensive guide explores the inner workings of AI agents, their core components, and the mechanisms that enable them to function autonomously while delivering measurable business value.
Understanding How AI Agents Work and Fundamentals
AI agents are autonomous software systems designed to perceive their environment, reason about goals and constraints, and take actions to achieve specific objectives. At their core, AI agents follow a fundamental cycle: they observe their environment, process information, make decisions, execute actions, and learn from the outcomes.
What makes AI agents special is how they combine all four parts—sensing, thinking, doing, and learning—into one smooth operation. They process huge amounts of data, make smart choices, take action, and keep getting better at it through continuous feedback loops.
Modern AI agents have a Large Language Model (LLM) at their core that acts as the system’s “brain.” These models help them understand the nuances of language, allowing them to process queries and give answers in plain, simple, human language while maintaining context throughout complex interactions.
The Core AI Agent Workflow
AI agents work through a continuous cycle of perception, reasoning, action, and learning. This process mirrors how humans approach decision-making, but at speeds and scales beyond human capability.
- Step 1: Perception AI agents start by gathering information from their environment through various inputs. Picture perception as the agent’s sensory system. This involves collecting and interpreting data from multiple sources, including text, sensor data, API responses, and database queries.
- Step 2: Reasoning After gathering data, agents process this information and analyze it to make decisions. This cognitive process involves using logic and available information to draw conclusions, make inferences, and solve problems. AI agents with strong reasoning capabilities can analyze data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions based on evidence and context.
- Step 3: Action The agent takes action by executing specific tools or functions based on their reasoning. This might involve calling APIs, updating databases, sending messages, or triggering other processes in the digital environment.
- Step 4: Observation and Learning The agent analyzes the results of their actions and incorporates this feedback into their knowledge base for future decision-making. This observation phase provides real-world feedback, confirming whether the action succeeded and providing needed details for continuous improvement.
Core Components of AI Agent Architecture
Large Language Models (LLMs)
At the foundation of modern AI agents are Large Language Models that serve as the reasoning engine. These models enable agents to understand natural language, process complex instructions, and generate human-like responses. The LLM acts as the “brain” of the agent, providing the cognitive capabilities needed for decision-making and problem-solving.
Contextual Memory Systems
AI agents maintain both short-term and long-term memory to track conversation history, user preferences, and learned behaviors. This memory system enables agents to maintain context across interactions and improve their performance over time through accumulated experience.
Memory components include:
- Working Memory: Temporary storage for current task information
- Episodic Memory: Records of past interactions and their outcomes
- Semantic Memory: General knowledge and learned patterns
- Procedural Memory: Knowledge of how to perform specific tasks
External Tools and Functions
AI agents extend their capabilities through integration with external tools, APIs, and systems. These tools allow agents to interact with databases, web services, calculation engines, and other applications to gather information and execute tasks beyond their base knowledge.
Common tool categories include:
- Information retrieval systems (search engines, databases)
- Communication tools (email, messaging, notifications)
- Computational tools (calculators, data processors)
- Action execution systems (workflow triggers, system controls)
Routing and Orchestration
The routing functionality determines which tools to use, when to use them, and how to coordinate multiple actions. This component enables agents to plan sequences of actions and manage complex workflows that involve multiple steps and decision points.
Advanced AI Agent Reasoning Methods
ReAct (Reasoning + Action) Framework
ReAct is a powerful method that blends step-by-step reasoning with action execution. This approach helps AI agents think systematically about their decisions before taking action. Tests show that ReAct cuts hallucination rates to just 6% compared to 14% with traditional methods.
ReAct’s three-step cycle includes:
- Thought Phase: The agent reasons about the current situation
- Action Phase: It executes a specific tool or function
- Observation Phase: It analyzes the results before proceeding
This methodical approach helps agents maintain better context and make informed decisions throughout complex task execution.
ReWOO (Reasoning Without Observation)
ReWOO builds on ReAct’s properties but addresses some key limitations by separating the reasoning process from external observations. This approach plans actions upfront instead of mixing reasoning and observation, which decreases token consumption and optimizes overall efficiency.
The ReWOO workflow consists of three modules:
- Planning Module: The agent anticipates its next steps given a user’s prompt
- Collection Stage: Gathering outputs from calling planned tools
- Execution Phase: Implementing the planned sequence of actions
Types of AI Agents and Their Capabilities
Simple Reflex Agents
These agents follow preprogrammed condition-action rules, typically in “if-then” format. When specific conditions are met, the agent executes corresponding actions. Simple reflex agents are effective for domain-specific use cases like fraud detection, where agents flag transactions based on predefined criteria.
Model-Based Agents
Model-based agents use memory and perception to store a current model of their environment. This state updates as the agent receives new information, enabling them to handle situations where the current state isn’t fully observable from sensor data alone.
Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents are designed to pursue specific objectives by considering the future consequences of their actions. They use search and planning algorithms to find action sequences that lead to desired outcomes, making them suitable for complex problem-solving scenarios.
Learning Agents
Learning agents can improve their performance over time through various machine learning techniques. They consist of four main components:
- Learning Element: Improves the agent’s knowledge through environmental interaction
- Critic: Provides feedback on response quality
- Performance Element: Selects actions based on learning
- Problem Generator: Creates proposals for new actions to explore
Real-World AI Agent Applications
Customer Service and Support
AI agents transform customer service by handling multiple types of inquiries simultaneously. Different agents can manage basic questions, complex technical issues, and escalation to human specialists when necessary. These agents track user activity and preferences in memory to provide personalized recommendations and support.
Business Process Automation
AI agents automate complex business workflows by coordinating multiple systems and processes. For example, a sales automation agent doesn’t just send follow-up emails—it tracks engagement, adapts messaging, and even reschedules meetings based on client availability and sentiment analysis.
Data Analysis and Reporting
AI agents can gather data from multiple sources, perform analysis, and generate reports automatically. They handle tasks like data collection, pattern recognition, trend analysis, and automated report generation while learning from user feedback to improve future outputs.
Supply Chain Management
In logistics, AI agents coordinate multiple aspects of supply chain operations. One agent might optimize delivery routes while another monitors inventory levels, and a third predicts potential disruptions. These agents work together to maintain optimal operations across complex supply networks.
Implementation Best Practices
Architectural Considerations
To implement an AI agent, organizations need to assemble four core components: LLMs, contextual memory, external functions or sub-agents, and routing functionality. Building agents can be done through custom code integration, but this approach doesn’t scale and is hard to maintain.
Framework Selection
Code-based agent development frameworks, like LangGraph and CrewAI, can reduce the learning curve but require dedicated development resources. No-code agent platforms provide visual interfaces, pre-built connectors, and scalable architecture that accelerate implementation for non-technical teams.
Evaluation and Monitoring
Successful AI agent implementation requires:
- Establishing evaluation metrics to measure performance
- Investing time in prompt engineering before advanced customization
- Prioritizing data quality and metadata for optimal performance
- Implementing guard rails and context filtering for safety
Advanced AI Agent Capabilities
Multi-Agent Collaboration
Modern AI agents can work together in coordinated systems where multiple specialized agents collaborate on complex tasks. Each agent focuses on specific domains while communicating and coordinating with others to achieve collective goals.
Self-Improvement and Adaptation
Advanced AI agents incorporate self-refining capabilities that allow them to learn from experience, adjust behavior based on feedback, and continuously enhance performance over time. This involves machine learning techniques, optimization algorithms, and automated refinement processes.
Tool Learning and Integration
AI agents continuously expand their capabilities by learning to use new tools and integrate with emerging systems. Tool learning involves teaching agents how to effectively use external resources by understanding their functionalities and appropriate application contexts.
How Isometrik AI Powers Intelligent Agent Systems
Isometrik AI‘s agent development platform provides comprehensive tools for building sophisticated AI agents that deliver business value. Our platform offers:
- Pre-Built Agent Templates: Industry-specific templates that accelerate development and reduce time-to-deployment
- Advanced LLM Integration: Seamless integration with cutting-edge language models and reasoning frameworks
- Scalable Architecture: Cloud-native infrastructure that grows with your business requirements
- Comprehensive Tool Libraries: Extensive collections of pre-built tools and API connectors
Our AI agent solutions help organizations implement intelligent automation that adapts to changing requirements while maintaining high performance and reliability standards.
Ready to Implement AI Agents in Your Organization?
Understanding how AI agents work is the first step toward implementing these powerful systems in your business operations. The combination of perception, reasoning, action, and learning creates unprecedented opportunities for automation and intelligent decision-making.
AI agents represent a fundamental shift from reactive tools to proactive systems that can understand context, plan actions, and continuously improve their performance. Organizations that master these technologies gain significant competitive advantages through improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Transform your business operations with Isometrik AI’s proven agent development platform. Contact our AI specialists today to discover how intelligent agents can revolutionize your organization through autonomous decision-making, continuous learning, and seamless integration with your existing systems.